
Tamanho desta previsualização: 600 × 600 pixels. Outras resoluções: 240 × 240 pixels | 480 × 480 pixels | 768 × 768 pixels | 1 024 × 1 024 pixels | 2 048 × 2 048 pixels | 4 700 × 4 700 pixels.
Imagem numa resolução maior (4 700 × 4 700 pixels, tamanho: 12,11 MB, tipo MIME: image/jpeg)
Este arquivo é do Wikimedia Commons e pode ser utilizado por outros projetos. Sua página de descrição de arquivo é reproduzida abaixo.
Descrição do arquivo
| DescriçãoTriton moon mosaic Voyager 2 (large).jpg |
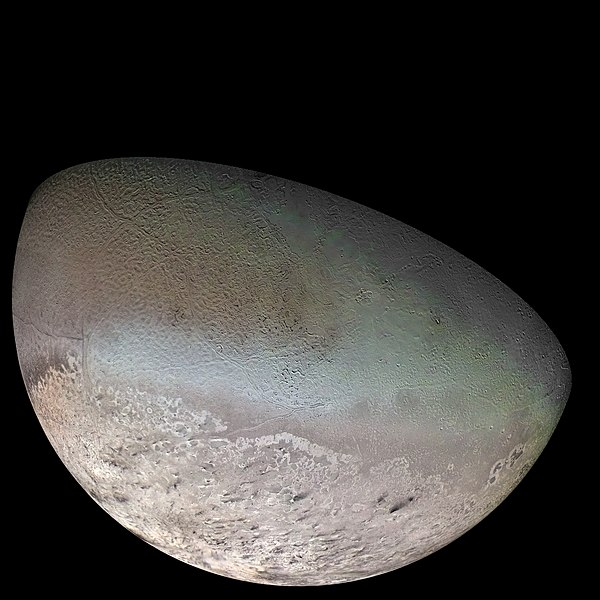
English: Global Color Mosaic of Triton, taken by Voyager 2 in 1989
Deutsch: Globales Farbmosaik von Triton, 1989 aufgenommen durch Voyager 2 |
| Data | |
| Fonte | http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00317 |
| Autor | NASA / Jet Propulsion Lab / U.S. Geological Survey |
English: original NASA caption: Global color mosaic of Triton, taken in 1989 by Voyager 2 during its flyby of the Neptune system. Color was synthesized by combining high-resolution images taken through orange, violet, and ultraviolet filters; these images were displayed as red, green, and blue images and combined to create this color version. With a radius of 1,350 km (839 mi), about 22% smaller than Earth's moon, Triton is by far the largest satellite of Neptune. It is one of only three objects in the Solar System known to have a nitrogen-dominated atmosphere (the others are Earth and Saturn's giant moon, Titan). Triton has the coldest surface known anywhere in the Solar System (38 K, about -391 degrees Fahrenheit); it is so cold that most of Triton's nitrogen is condensed as frost, making it the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a surface made mainly of nitrogen ice. The pinkish deposits constitute a vast south polar cap believed to contain methane ice, which would have reacted under sunlight to form pink or red compounds. The dark streaks overlying these pink ices are believed to be an icy and perhaps carbonaceous dust deposited from huge geyser-like plumes, some of which were found to be active during the Voyager 2 flyby. The bluish-green band visible in this image extends all the way around Triton near the equator; it may consist of relatively fresh nitrogen frost deposits. The greenish areas includes what is called the cantaloupe terrain, whose origin is unknown, and a set of "cryovolcanic" landscapes apparently produced by icy-cold liquids (now frozen) erupted from Triton's interior.
Deutsch: Ursprüngliche Überschrift der NASA: Globales Farbmosaik von Triton, das 1989 während des Vorbeiflugs am Neptun abgelichtet wurde. Die Farbe wurde durch Kombination von hochauflösenden Bildern, die durch orange, rote, violette und ultraviolette Filter aufgenommen wurden, zusammengesetzt; diese wurden in rote, grüne und blaue Bilder umgewandelt und dann zusammengefasst, um ein Farbbild zu generieren. Mit einem Radius von 1350 km, etwa 22 % kleiner als der Erdmond, ist Triton der mit Abstand größte Mond Neptuns. Er ist einer von nur drei Objekten im Sonnensystem, die eine stickstoffdominierte Atmosphäre aufweisen. (Die anderen zwei sind die Erde und der große Saturnmond Titan.) Triton hat mit 38 K (−235 °C) die kälteste bekannte Oberfläche im ganzen Sonnensystem. Er ist so kalt, dass der Großteil des Stickstoffs als Frost kondensiert ist. Das macht ihm zum einzigen Satelliten im Sonnensystem, von dem man weiß, dass seine Oberfläche hauptsächlich aus Stickstoffeis besteht. Die rosafarbenen Ablagerungen bilden eine massive Südpolkappe. Diese besteht wahrscheinlich aus Methaneis, das unter Sonnenlicht zu roten und rosa Verbindungen reagiert hat. Die dunklen Streifen, die das rötliche Eis überlagern, könnten eis- und vielleicht kohlehaltiger Staub sein, der von riesigen geysirartigen Rauchfahnen abgelagert wurde. Von diesen Geysiren wurden einige aktive durch Voyager 2 beobachtet. Das blaugrüne Band, das im Bild sichtbar ist, erstreckt sich entlang des ganzen Äquators. Es könnte aus relativ frisch gefrorenen Stickstoffablagerungen bestehen. Die grünlichen Gebiete beinhalten das sogenannte „Cantaloupe-Terrain“ (benannt nach der Melonenart), dessen Ursprung unbekannt ist, und eine Reihe von „kryovulkanischen“ (eisvulkanischen) Landschaften, die anscheinend von eisig kalten, nun gefrorenen Flüssigkeiten stammen, die aus Tritons Innerem ausgebrochen sind.
Licenciamento
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| Esta obra encontra-se no domínio público porque foi criada pela NASA. A política de direitos autorais da NASA diz que "o material da NASA não é protegido por direitos autorais a não ser quando especificado". (página sobre direitos autorais da NASA ou Política de uso de imagens da JPL). |  | |
 |
Avisos:
|
Legendas
Adicione uma explicação em uma linha sobre o que este arquivo representa
Triton portrayed by Voyager 2 in 1989
Triton, Voyager 2:en kuvaamana vuonna 1989
Globales Farbmosaik von Triton, 1989 aufgenommen durch Voyager 2
Itens retratados neste arquivo
retrata
25 agosto 1989
image/jpeg
Histórico do arquivo
Clique em uma data/horário para ver como o arquivo estava em um dado momento.
| Data e horário | Miniatura | Dimensões | Usuário | Comentário | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| atual | 19h40min de 10 de outubro de 2011 |  | 4 700 × 4 700 (12,11 MB) | wikimediacommons>Jbarta | Minimally compressed JPG from TIFF original at NASA. This image has already been colored by NASA. I think we have no business trying to "fix" the coloring. The only alteration made from the NASA original is to enlarge the canvas to enclose the complete sp |
Uso do arquivo
As seguintes 3 páginas usa este arquivo:
Metadados
Este ficheiro contém informação adicional, provavelmente adicionada a partir da câmara digital ou scanner utilizada para criar ou digitalizar a imagem. Caso o ficheiro tenha sido modificado a partir do seu estado original, alguns detalhes poderão não refletir completamente as mudanças efetuadas.
| Comentário de arquivo JPEG | Minimally compressed jpg from tiif original at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00317 |
|---|



 " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="O que estudar para o enem 2023">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="O que estudar para o enem 2023"> " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Qual melhor curso para fazer em 2023">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Qual melhor curso para fazer em 2023"> " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Enem: Conteúdos E Aulas On-Line São Opção Para Os Estudantes">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Enem: Conteúdos E Aulas On-Line São Opção Para Os Estudantes"> " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Como Fazer Uma Carta De Apresentação">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Como Fazer Uma Carta De Apresentação"> " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Como Escrever Uma Boa Redação">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Como Escrever Uma Boa Redação"> " class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Concurso INSS edital 2022 publicado">
" class="attachment-atbs-s-4_3 size-atbs-s-4_3 wp-post-image" alt="Concurso INSS edital 2022 publicado">


